HTML Vocabulary
Hyper Text Markup Language (HTML) defines the structure of a website and is XML based.
Angle Bracket
Angle brackets consists of an opening element (<) and a closing element (>).
Tag
A tag is an HTML keyword surrounded by angle brackets.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<title></title>
</head>
<body>
</body>
</html>
Attribute
HTML tags use attributes to declare special values or store data. Attributes belong inside the angle brackets such as the href attribute inside of an anchor tag and use the following syntax: attribute="value"; it is convention to ensure there are no spaces between the equal sign and to use quotation marks. Single quotes may be used but typically are never used.
A tag with multiple attributes have them split with a single space or a new line (if the tag is too long). HTML is not sensitive to whitespace so take advantage of this to ensure your code is easy to read.
<a href="#" title="I'm a title">Click me!</a>
Parents & Children
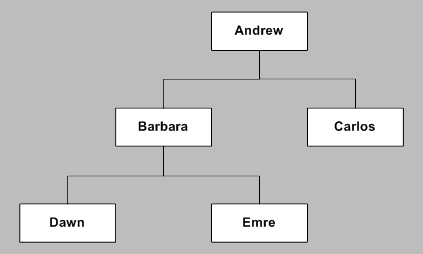
HTML elements are nested and can be seen as a family tree. In the above example, Andrew would be the parent and Barbara would be a child of Andrew. The same would apply to code and is based on what elements are inside each other. Keep in mind, just because an element is a child, that does not mean that it cannot also be a parent to more elements (e.g. Barbara is the parent of Dawn).
<div class="parent">
<div class="parent child">
<div class="child grandchild"></div>
</div>
<div class="child"></div>
</div>